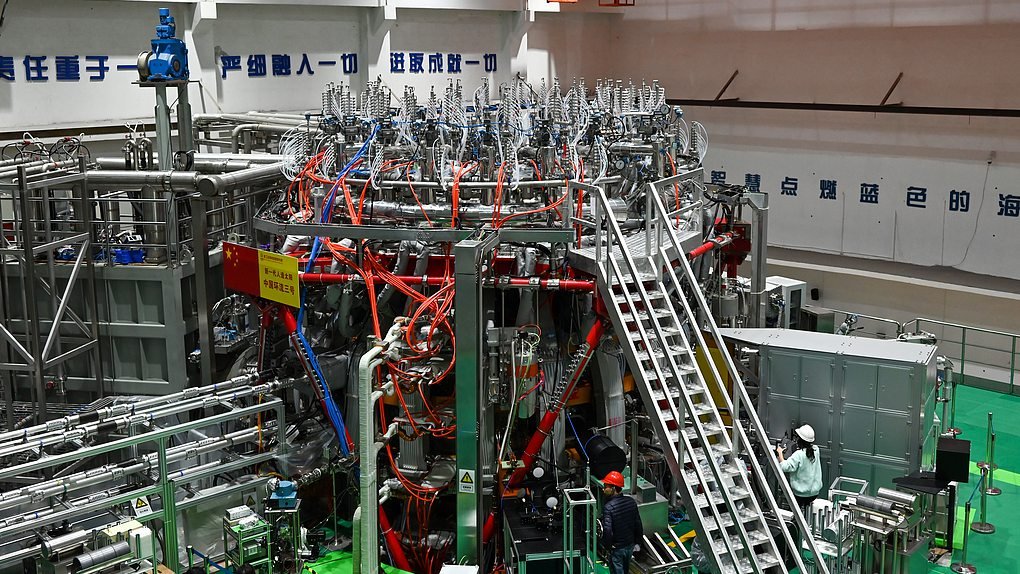
China has recently advanced its nuclear fusion research with the Huanliu-3 (HL-3) tokamak, a state-of-the-art device in their “Artificial Sun” series. This new phase of experiments includes, for the first time, a digital twin system created by the China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC).
According to the CNNC, this innovative system brings a virtual dimension to the physical experiments, enhancing control and precision.
The HL-3 is a magnetic confinement fusion facility, marking China’s largest and most sophisticated approach to achieving controlled nuclear fusion. One of the critical procedures in its operation is the vacuum chamber “baking” process, essential for producing an environment fit for nuclear fusion.
In this phase, the digital twin functions as a monitoring and simulation tool. By creating a virtual model of HL-3’s physical components, it provides real-time updates and highly accurate data on the status of the vacuum chamber, significantly boosting operational efficiency. This system enables immediate calculations and tracking, allowing for responsive control throughout the entire fusion process.
Introducing the digital twin technology is a crucial step forward in HL-3’s digital management. It ensures the facility operates safely and efficiently while opening doors to smarter, integrated control options for the future. This tech could also have extensive applications in other advanced fields, according to CNNC.
Chinese researchers continue to explore the capabilities of digital twin technology within nuclear fusion science, aiming to elevate HL-3’s role in global energy solutions. Following its opening for international collaboration last year, the HL-3 has attracted global interest. This year, it welcomed partnerships from 17 major research institutes and universities worldwide, including teams from France and Japan. Together, they achieved a new breakthrough—a unique magnetic field structure, a world-first in fusion research.






I can’t believe if it is possible
Wao! Amazing and wonderful project